| Theme | Acid-Base Reaction. Newton's Laws |
| Category | Science Experiments, Experiments for children |
| Main product | Citric Acid, Sodium Bicarbonate. See below for where to find them. |
| Short description | In this fun experiment, we will also be able to experience the Newton's third law. On a very small scale, this experiment will simulate how rockets fly. As fuel we will use a mixture of citric acid and sodium bicarbonate. When both are mixed together with water, they generate a reaction (acid-base reaction). In the reaction between the citric acid and baking sodaa gas, CO2, is generated. In the case of an airtight or semi-airtight container, this gas expands inside the container, putting pressure on the lid and causing the container to fly away. |
EXPERIMENTAL MATERIALS
- Cylindrical container with an airtight pressure lid. This is probably the most difficult material to find. I have tried several and finally in this parapharmacy I found a container with an airtight lid that works very well for the experiment: Container - Lid Buy Vessel – Buy Cover
- Citric Acid (where to buy)
- Sodium bicarbonate (where to buy)
- Paper napkin
- Water
STEP-BY-STEP EXPERIMENT
STEP 1. Take a cylindrical container and place a finger of water in it. We use a 25ml beaker and put 5ml of water in it.

STEP 2. Put a layer of napkin on top.

STEP 3. Pour baking soda and citric acid on top. About half and half.

STEP 4. Close the lid tightly. It is very important that the lid is tightly closed.

STEP 5. Turn the jar upside down and let the napkin get wet, mixing the water with the acid and baking soda. The reaction between the citric acid and the baking soda will start. This reaction releases CO2, expanding the air inside the canister until the lid cannot hold, explodes (in a very controlled way) and the canister goes up like a rocket.


TECHNICAL EXPLANATION OF THE EXPERIMENT
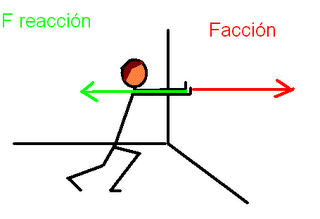
In a rocket the fuel is paraffin or liquid hydrogen, and the thrust of the rocket is produced by the vertical reaction of the gases emitted against the atmosphere.
Both processes correspond to Newton's third law, which we will state: "if object A exerts a force on object B, then object B must exert a force of equal magnitude in the opposite direction on object A".
WHAT YOU ARE APPLYING WITH THIS EXPERIMENT
This experiment is not only great fun for children, but you are also applying it:
- Newton's third law
- Acid-base reaction chemistry
